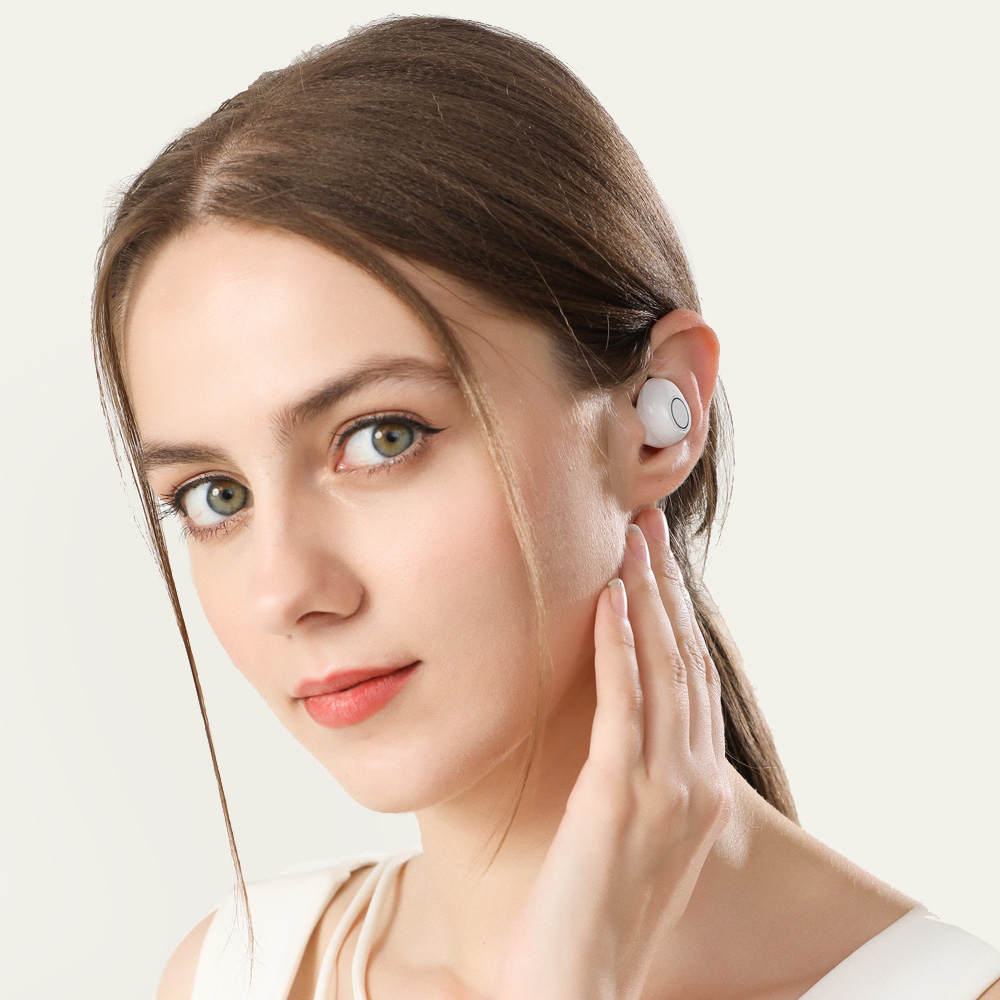
JH-A39
Mini ITE
Rechargeable
Hearing Aid Amplifier
Easy controls, Fashion, Rechargeable
One button volume control, earbud design, discreet in the ear hearing aids.


Huizhou Jinghao Medical Technology company specialized in the production of hearing AIDS, atomizer, air cushion and other health care products professional company.

Factory area covers more than 35000 sqm. The best hearing aids manufacturer in China.

Our customer support is second to none – users rave about how we don’t rest until every issue is solved to their satisfaction.
for OEM order , Our normally lead time is 7-15days.
Loyal customers, they don’t just come back, they don’t simply recommend you, they insist that their friends do business with you.
Just received my hearing aid and so far love it very easy to set up they are set up for the left ear but easy switch it’s nice to hear again I’m thinking of getting the other one


I started having tinnitus in 2017, which caused hearing loss.I was born with the Blomed hearing aid from the hearing foundation, which improved my hearing.I can’t hear anything without a hearing aid.When I put on the hearing aid, it will amplify the sound and reduce the tinnitus degree, and when I am with my family and friends, I can also have normal communication, and there will be no more pain like deaf people, I am very happy.This is the best gift I have received.…

Some of our typical hearing aids customers , we can do OEM service for medical device manufacturers/importers, Audiology clinic, pharmacy, or hearing aids onliner sellers .






Once hair cells in the inner ear are dead, there’s no bringing them back. But hearing aids may significantly improve your ability to hear by making sounds louder and easier to understand.
Hearing aids have a microphone to pick up sound, an amplifier to make sound louder, and a receiver that sends the sound into the ear canal. In modern digital aids, microphones transmit sound to a computer chip, which adjusts the volume and amplifies the sound frequencies needed to help improve your hearing. (Though analog aids are less common and less complex than digital aids, they do have advantages, including fewer advanced features. That can make them more user-friendly.)
A hearing professional can program a digital aid to filter out wind and other background noise, as well as fine-tune the aid to match your specific hearing loss pattern. More and more models can sync wirelessly with your smartphone, enabling you to take calls, stream audio, and even adjust your aid’s settings using an app.
The right hearing aid for you depends on several factors, including the type and severity of your hearing loss, your lifestyle, and your manual dexterity. However, a hearing aid that one person likes might not work for someone else, even if both have almost identical audiograms (charts that show the degree of hearing loss for low-, middle-, and high-pitched sounds).
Most hearing aids will never completely remove background noise and allow you to hear only the person—or people—talking. “It’s going to bring people back to hearing, but because of the way we process sound, it’s not going to bring them back to normal hearing,” says audiologist Patricia Chute, Ed.D., provost and vice president for academic affairs at Dalton State College in Dalton, Ga.
And even within the same brand, there can be several versions of a given model. That kind of variation makes comparing hearing aid models and brands very challenging.
Digital hearing aids come in five major styles and are categorized by where on or in the ear they’re worn. In spring 2018 we asked more than 122,000 Consumer Reports members about their experiences with hearing loss and hearing aids. The majority (71 percent) of the hearing aids were mini-behind-the-ear types.
Pros: Comfortable, barely visible. Prevents a plugged-up feeling (especially when using an open ear tip, which is appropriate if you can hear well in the low pitches). Larger versions are easy to insert.
Cons: Wax and moisture buildup may limit the life of the receiver. Does not allow for significant amplification, especially in the low frequencies.
In this group of aids, which sometimes includes RITA hearing aids, all electronic components are in the plastic case worn behind the ear. Sound is sent to the ear through the tubing that connects the case to the receiver and a custom earmold worn in the ear canal.
Pros: Offers flexible features and considerable low- and high-frequency amplification, making it good for those with severe hearing loss. On larger, traditional models, controls are easy to manipulate and the telecoil mode is easily selected and used (see below for more information on the telecoil). The custom-made earmold can be easily cleaned. Accommodates larger batteries for more power. Feedback is rare because of the snug fit.
Cons: Some custom molds are visible (clear molds are not). Vulnerable to sweat and wax buildup, but the tubing and mold are easily cleaned. The earmold must fit snugly and fill the entire ear canal, which can cause a plugged-up feeling.
Pros: Recessed into the ear canal and fits deep and tight in the ear. Minimal feedback when used with a phone. Because it’s in the canal, it has low visibility and can be removed with a removal string. Less sensitive to wind noise.
Cons: Too small to include a directional microphone (which reduces background noise by picking up sound from a specific direction) but often has some directional sensitivity. Ear might feel plugged up unless hearing aid is vented. Vulnerable to wax buildup and moisture. It can accommodate only a small battery, so battery life is relatively short. Because of their small size, the batteries can be difficult to insert and remove. The aid may be challenging to handle and adjust.
Pros: Barely visible, less of a plugged-up feeling because the aid sits deep in the canal. Larger units can include directional microphones.
Cons: Discomfort is a problem for many, along with the concerns that are typically associated with completely-in-the-canal models. These models are susceptible to moisture, and the receiver is vulnerable to clogging from earwax. The battery tends to be small, so battery life is relatively short. May be challenging to handle and adjust.
All electronic components are included within the case, which rests in the bowl of the outer ear.
Pros: Offer more room for features such as telecoil, directional microphone, and wireless streaming. Less of a plugged-up feeling when vented. Relatively easy to insert.
Cons: Some people consider ITE units to be more visible, and the telecoil might not be as powerful as those on BTE hearing aids because it is smaller in size.
In our survey, 53 percent of people who wear hearing aids said that rechargeable batteries were one of the most important features they looked for when purchasing a hearing aid. Smartphone capabilities or tinnitus masking was noted as most important by 43 percent, and 42 percent said automatic noise level adjustment was most important.
Forty-one percent said that the option of multiple program settings (which allows users to optimize aids for a variety of environments, such as quiet rooms or loud restaurants) was one of the most important features they looked for. Forty percent mentioned advanced microphone features, and 37 percent said wireless connectivity to other devices was most important. Other key features, according to hearing aid experts, include the following:
Telecoil
An option on many modern hearing aids, a telecoil is a small sensor or copper wire that is placed in the hearing aid. When activated, it wirelessly picks up a magnetic signal from hearing-aid-compatible telephones and public address systems—such as those that may be in conference rooms, concert halls, museums, taxis, and even subway trains—and converts that energy into sound. An audio induction loop, or hearing loop, which is a wire that circles a telecoil-compatible room or space, emits the signal that the telecoil picks up.
Such technologies help people—especially those with moderate to profound hearing loss—to better understand a speaker’s voice by making it louder and eliminating most background noise and reverberation. Ask your provider for a manual T-switch, which enables seamless connection to loop systems. He or she should also activate your telecoil and show you how to use it.
Directional Microphone
Many modern hearing aids have a directional microphone, which helps you converse in noisy environments by making the audio signal in front of you louder than the noise from the rear or sides. This technology works best when you are close to the sound source. Almost all hearing aids with this feature are able to automatically switch between directional and omnidirectional settings, depending on the environment. Advanced versions can focus behind the listener or to the listener’s side. A negative: It’s prone to picking up wind noise.
Feedback Suppression
Feedback suppression, or digital feedback reduction, helps quell high-pitched whistling sounds. Most modern hearing aids include this feature, but its effectiveness differs from aid to aid. It’s useful for minimizing feedback if you’re close to the telephone or if the aid is slightly dislodged from your ear when you move your jaw. It can also allow for much more venting, comfort, and better sound quality for listeners who have good hearing in the lowest pitches. A proper fit can also reduce feedback.
Digital Noise Reduction (DNR)
Improves listener comfort and communication in noisy environments by blocking out some background noise. This makes it easier to hear and understand speech, though it is not a fix for all situations.
Other Hearing Aid Features Worth Noting
Most newer aids also have low-battery indicator sounds, wax guards to prevent buildup, automatic and manual volume control, wireless connectivity between hearing aids, data logging, and a memory of your listening preferences. Another newer feature is direct audio input, which allows users to connect directly to a television or another electronic device.
At the higher end, Bluetooth wireless technology allows users to stream music and calls from computers, smartphones, and TVs directly through their hearing aid. Some aids also have frequency shifting technology (for those with hearing problems in the highest pitches) and accessories such as remote microphones (sometimes called “spouse mics”), advanced smartphone remotes, and more.
More than 60 percent of the survey respondents who use hearing aids waited two years or longer after noticing a hearing loss to buy an aid; 42 percent of them blamed high prices. If you need an aid but worry about the cost, these tips can guide you to some affordable solutions.
1. Check out your coverage. Most insurance does not cover hearing aids, though some children, federal workers, and veterans, as well as residents of Arkansas, Connecticut, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island, can get them covered. A few plans, including some from Medicare Advantage, offer at least partial coverage or discounts.
If you have a high-deductible insurance plan, you can put up to $3,450 per individual or $6,900 per family in a health savings account to pay for aids with pretax dollars. (If you are 55 or older, you can contribute an additional $1,000 to an individual or family plan.) With a flexible spending account, you can use up to $2,700 in pretax dollars for aids, batteries, and maintenance.
2. Get a detailed written contract. Make sure your contract allows you to return your aids and get most of your money back if you’re not satisfied. It should also detail the length of the trial period, the length of the warranty and what it covers, adjustment services, loss and damage insurance coverage, and what exactly is included in the price you’re given.
3. Buy only what you need. Bluetooth capability is a convenient extra, but it can add hundreds of dollars to your bill. If you don’t think you’ll use it, skip it.
Economy hearing aids may provide what you need. Ask your provider to compare your performance on speech-in-noise tests using a premium aid and an economy aid. The provider should also help you determine how much, if anything, your insurance will pay.
4. Ask for a price break. Though only 14 percent of hearing aid users in our survey tried to negotiate a lower price, almost half were successful when they did. So wherever you buy, try bargaining or asking for a lower-priced model.
Note that some audiologists may carry only a few brands, which can limit your ability to comparison shop. Ask your provider to explain why he or she recommends one brand over another and the pros and cons of each.
5. Look for bargains. Costco offers free screenings at select locations and very competitive prices on hearing aids. Only certain stores have on-site audiologists or hearing specialists, so make a phone call before you go; appointments are a must.
Buying aids online can help you save as well, but you may have to send them back for adjustments or pay a local hearing specialist to help you.
6. Seek out organizations that may offer assistance. A number of government, state, and independent groups, such as the Lions Clubs, may help you pay for hearing aids or offer discounts.
When You Pick It Up
Ask your hearing aid provider to do a real-ear test, also called a real-ear measure. This involves placing a thin probe in your outer ear while you wear your hearing aid—to measure whether your hearing aid is responding appropriately to your level of hearing loss. He or she should also test your understanding of speech in both quiet and noisy areas.
The provider should ensure that the aid is comfortable. He or she should explain how to use, clean, and store it; where to buy batteries in the correct size; how to store, change, or recharge batteries; and how to minimize squealing and feedback. He or she should also go over the importance of keeping the aid dry and of removing it before radiological or other diagnostic testing.
Speak up about any discomfort or difficulties with use, and practice talking on the phone while you’re in the office. Your provider should make any adjustments while you wait.
Office staff should schedule a follow-up and check in with you by phone a few days after the fitting. If the hearing aid is not comfortable or helpful, the provider can make adjustments.
Also, make sure that your aid is compatible with your cell phone and cordless phones and that the T-switch is enabled. Discuss using your hearing aid with assistive listening devices such as FM and infrared systems and hearing loops. If your hearing aid comes with a smartphone or smartwatch app, make sure you know how to use it.
At Home With a New Hearing Aid
Practice everyday activities using your new hearing aid and be aware that it takes time to adjust. Some sounds might seem too loud at first because your brain isn’t used to processing sounds you haven’t heard in a long time. If you’re unsure whether your hearing aid is working as well as possible, take it in for an adjustment, especially if your voice sounds funny or if your ear feels clogged.
If you think you have a problem but aren’t ready to spend thousands on hearing aids, consider these cheaper alternatives:
Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs)
These over-the-counter products, which generally have fewer features and less functionality than hearing aids, may offer a lower-cost solution for some people with situation-specific hearing difficulty. PSAPs, which are designed for people who want to amplify certain sounds, cannot be marketed as devices that can help people with hearing loss (because they aren’t subject to the same standards as hearing aids). When purchasing a PSAP it is helpful to ask an audiologist or a dispenser to test the device to make sure it is suitable for your hearing loss (not dangerously loud for you, for example, and able to amplify speech in the frequencies where you have hearing loss).
It might be helpful to know that a law passed in 2017 calls for the creation of a new category of hearing aids. These will be sold over-the-counter but will legally be considered hearing aids, and they’ll be aimed at those with mild to moderate hearing loss. (Note that the FDA has three years from the law’s passage to come up with rules for which products will fall into this new category, what their technical specs must be, and how they’ll be labeled and marketed.)
To find out whether PSAPs can help, we tested two cheaper models ($20-to-$30 range) and two higher-end ones ($200 to $350). Three CR employees with mild to moderate hearing loss used these PSAPs at home, at work, and in our lab, where we tested how well the devices could assist with hearing conversations in a noisy environment. An outside hearing aid expert also assessed each device in areas such as amplification, battery and microphone function, and sound distortion.
With the right fit and adjustment, we found that the higher-end models can help those with mild to moderate hearing loss, especially when watching TV. Some adjustable models can even have the same functionality as an entry-level hearing aid. But beware the penny-saver PSAPs: The cheaper options didn’t measure up, and more important, our expert found that they could potentially damage hearing if used long-term—by over-amplifying some loud sounds, such as a fire engine siren.
Other Assistive Listening Devices
If you need just a little help with hearing, a number of other lower-cost listening options are available. These include apps that let you amplify sound with your smartphone and earbuds, and portable wireless devices that let you listen to your TV and other audio devices with earphones. You can also find amplified, flashing, and vibrating versions of basic household items such as telephones, alarm clocks, and doorbells.
