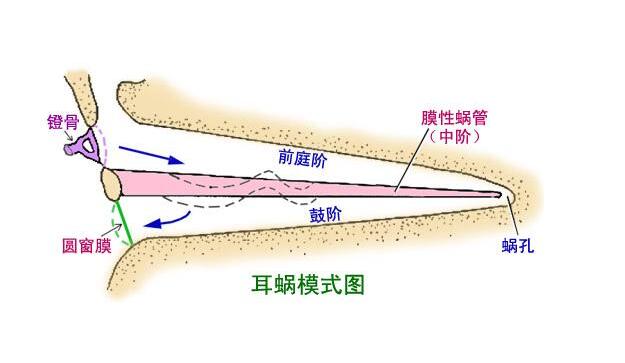
The cochlea is a spiral tube containing sensory cells. The cochlea decomposes the sound by frequency and is then converted by the sensory cells into neural codes within the auditory nerve. Common causes of hearing loss and tinnitus caused by cochlear injuries are as follows:
Meniere’s disease Meniere’s disease is a progressive disease defined as a periodic vertigo episode, a fluctuation in sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus and fullness of ear swelling.
In the early stages of the disease, hearing loss only affected low frequencies and was almost completely reversible. But as the disease progresses, the remaining hearing eventually worsens and spreads to a higher frequency. Symptoms begin to be unilateral, but in many patients, depending on the course of the disease, the contralateral ear is involved after 10 or 15 years. Tinnitus may persist between acute episodes, but generally worsens two days before the day of dizziness.
Cochlear blood flow changes The cochlea needs an appropriate blood supply to maintain its function. The labyrinth artery is a terminal artery and there is no blood supply to the inner ear. Even a slight change in blood perfusion can cause cochlear damage. In addition, the cochlear’s high energy consumption depending on the blood supply makes it vulnerable and requires excellent cochlear fluid balance.
Many systemic diseases that cause hearing loss are also associated with tinnitus, if those are caused by changes in circulation or microcirculation. Many hypotheses are proposed to explain the pathology of sudden hearing loss without any other symptoms. One hypothesis is that blood vessels are damaged. Although no conclusive evidence has been found, it has been suggested that a viral infection, that is, a virus attacking endothelial cells, causes a sudden hearing loss. Hearing loss can be extremely severe at first, and often accompanied by tinnitus. Hearing may worsen within a few hours. Fortunately, tinnitus is almost always limited to one ear and has a good spontaneous recovery almost.
The hearing function is generally spontaneously recovered in 1/3 patients, 1/3 is improved, and there is no change in the remaining patients. In some cases hearing will improve and tinnitus will remain the same. Different treatments such as steroids, antiviral drugs or hyperbaric oxygen are used.
Barotrauma Tinnitus may occur after diving or during flight, especially if you have a cold or allergy. In these cases, a barotrauma may cause symptoms because of a sudden change in air pressure that affects the cochlear fluid. Tinnitus may be temporary or it may be continuous. If the wound is so severe that it causes rupture of the tympanic membrane or rupture (leakage) of the round window, resulting in hearing loss and/or dizziness, tinnitus often occurs. For restoring hearing and relieving tinnitus, proper medical or surgical treatment is required.
Head trauma Tinnitus and balance symptoms are common after mild and severe head trauma. A fracture of the tibia may occur after head trauma, causing cochlear damage with severe hearing loss, dizziness, and tinnitus. Acute vertigo usually lasts for a few days and then relieves, but dizziness may persist. Hearing loss is often permanent, and tinnitus may be reduced or continued with hearing loss.
Head trauma without a fracture of the tibia may cause cochlear damage with symptoms such as dizziness, tinnitus, and sometimes hearing loss. These symptoms may last for a few months and then gradually disappear, while tinnitus often continues. The mechanism by which shocks cause hearing impairment is not fully understood. It has been suggested that more advanced neural structures are involved.
Head trauma can also cause blood to seep into the tympanic cavity and rupture of the tympanic membrane and dislocation of the ossicular chain, leading to conductive hearing loss and tinnitus. These injuries often require proper surgical treatment.
Jinghao medical hearing aid reminder:Hearing aids need to be professionally “fitted”. It is very important to choose a professional hearing aid fitting center and hearing aid fittings! You can call the Jinghao medical for any hearing problems, or you can come to the center to experience the experience. . Hearing aid free consultation phone: +86-18566295705
You can also scan our WeChat public account for more information about hearing.