What is hearing impairment?
Hearing impairment, commonly known as deafness, refers to various reasons that make people’s hearing difficult, unable to hear or hear the sound of the environment and speech.
The degree includes the following:
Mild: It is difficult to listen to the conversation
Moderate: It is difficult to listen loudly
Severe: shouting at the ear can only hear a few words
Extremely heavy: shouting at the ear and hearing no words
Hearing impairment directly affects people’s life, work and study; for children, it can affect the development of their language ability. In severe cases, they may be dumb.
What are the high-risk groups for hearing impairment?
Family history of deafness
Have had other history of ear diseases, such as otitis media, Meniere’s disease
Long-term exposure to noisy environments
History of application of ototoxic drugs
Suffering from chronic systemic diseases such as high blood pressure, high blood fat, diabetes
Have bad habits, such as smoking, drinking
Long-term mental stress
How to prevent hearing impairment
Different precautions can be taken depending on the cause of the hearing impairment and the patient population. If there are deafness members in the family, it is necessary to pay attention to whether the deafness gene diagnosis can be diagnosed as hereditary deafness to take measures to prevent other members from deafness.
Pregnant women should strengthen nutrition and reduce infection during the first trimester of pregnancy. Avoid using ototoxic drugs during pregnancy. High-risk pregnant women also need to strengthen their own and fetal monitoring to avoid hearing loss in newborns.
Active prevention and treatment of otitis media. Prevent sewage and foreign matter from entering the external auditory canal. Do not arbitrarily rub your ears and pay attention to ear hygiene. In the event of otitis media, seek medical advice promptly.
Try to stay away from noise or reduce noise exposure time to prevent noise deafness.
The elderly should establish a healthy diet and living habits, and actively treat chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia to prevent senile deafness.
Use ototoxic drugs with caution to prevent drug-induced deafness.
What is the prenatal genetic diagnosis of deafness?
There are many factors that affect neonatal hearing, and heredity is one of the most important reasons. Prenatal diagnosis of deafness is currently one of the most effective means of preventing neonatal hereditary deafness. The prenatal diagnosis of deafness is to use the deafness gene diagnosis technology to clarify the cariogenic genes carried by the parents and the risk of the offspring. Before the birth of the fetus, according to the different pregnancy stages, the corresponding fetal tissue is taken to understand the condition of the fetal deafness gene. Whether it is a diagnosis of hereditary deafness. If a couple has already given birth to a deaf child, be sure to have a molecular diagnosis of the child before birth, and then consider the re-pregnancy problem after a diagnosis.
At present, the prenatal diagnosis of deafness carried out in clinical work is mainly an invasive prenatal diagnosis. According to the difference of gestational weeks when pregnant women come to the clinic, different parts are selected to extract fetal genetic material. Because deafness is not life-threatening, combined with ethical considerations, pregnant women over 28 weeks are not recommended for prenatal diagnosis of deafness. As technology advances, non-invasive prenatal diagnosis will be applied to the clinic in the near future.
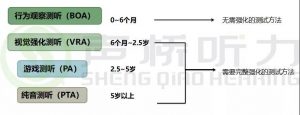
What is the procedure for newborn hearing screening?
Hearing screening (primary screening) should be performed after the baby is 72 hours after birth. If the initial screening fails, it should be re-screened in 42 days. If the baby fails to pass the screening, the child should be referred to the hearing diagnosis center within 3 months. A baby who has high risk factors for hearing loss at birth (such as jaundice, hypoxia, etc.) and a baby who has failed to pass the screening, is directly referred to the hearing diagnosis center within 3 months of the age.
If the baby passes the newborn hearing screening, the current hearing function is normal, but the risk of late hearing loss cannot be ruled out. Therefore, 0 to 6 babies should be screened by the child care organization every year.
What are the key ages for preschool children’s hearing screening?
The 2013 National Health and Family Planning Office issued the “Technical Specifications for Children’s Ear and Hearing Care”, which stipulates that children should also perform ear and hearing care at the same time as they pass the screening test during neonatal screening, including 6, 12, 24. And 36 age is the key age for hearing screening.
Children who pass hearing screening at birth may experience hearing loss at various stages of growth and development, which may have a serious impact on children’s speech development and learning. Therefore, hearing screening in childhood is essential!
Jinghao medical hearing aid reminder:Hearing aids need to be professionally “fitted”. It is very important to choose a professional hearing aid fitting center and hearing aid fittings! You can call the Jinghao medical for any hearing problems, or you can come to the center to experience the experience. . Hearing aid free consultation phone: +86-18566295705
You can also scan our WeChat public account for more information about hearing.

Link:Understand hearing impairment and prevent deafness
REF: Hearing Aids, Bluetooth Hearing Aids, Hearing amplifierThe article comes from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact [email protected] to delete it.