The ear function is more than you think. These functions are the basis for understanding the voice, listening to music and sound, and recognizing the position. As long as you close your eyes, you can understand that directional hearing is a very important indicator of familiarity with the environment. Having healthy listening ensures that you can enjoy a rich life anytime, anywhere, and you will have more in-depth experience with safety. To get a deeper understanding of hearing loss, it’s important to understand how hearing works. The ear is a simple but wonderful organ that transforms the sound waves in the air into a variety of meticulous sounds that are transmitted to your mind. It also conveys the emotions of the outside world to your heart.
Our ears are highly complex organs, mainly composed of three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
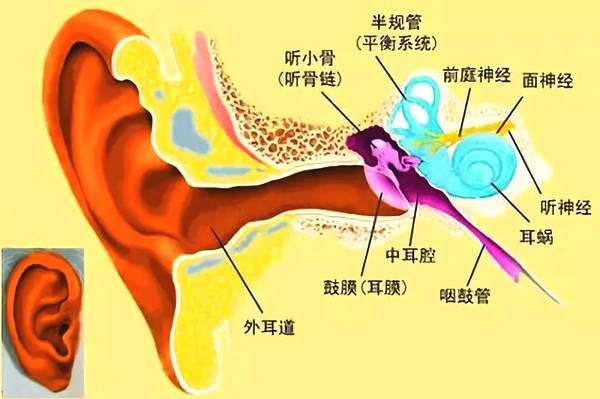
Auditory operation
Our ears collect sound, mechanically transmit, convert nerve signals to produce hearing, and let the brain recognize sounds such as music, shit, water, ringing, talking, etc. in one go.
external ear
It is the ear that we usually see, including the auricle and the ear canal; the sound is the sound wave that is transmitted to our ears through the air. The sound waves are collected through the auricle and transmitted through the ear canal to the eardrum in the ear. The eardrum is a round and elastic membrane that will vibrate when there is sound coming in.
Middle ear
This is a cavity filled with air that is separated from the outer ear by the eardrum (ie the tympanic membrane). There are three small bones in the middle ear: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes, which are the three smallest bones in the human body. The small bone is the conduction bridge between the eardrum and the inner ear. The mechanical vibration generated by the three small bone chains connected to the small bones causes the liquid in the cochlea to fluctuate, which in turn stimulates the nerve fibers to generate nerve signals.
inner ear
The inner ear mainly refers to the cochlea, which is derived from the Greek snail or spiral. Its appearance is like a snail. Its interior is filled with liquid. When the sound is transmitted through the small bone, the liquid will undulate and stimulate the nerve fiber. The hair cells generate nerve signals and transmit these signals to the auditory nerve, which are then uploaded to the brain to interpret the signals as sound.
Loudness
Small to almost inaudible sounds, loud to the sound of the sky, the ears can be received, the difference is the loudness and distance of these sources. By listening, it is also possible to accurately determine the position and direction of the sound source, which is the so-called listening position.
The intensity of the sound is in decibels (dB). Decibel represents the unit of relative intensity of sound. We define the weakest sound that can be perceived by the average human ear as 0 decibels. It is also the smallest sound that can be heard by young people with good hearing. The volume of daily conversation is about 50 decibels to 60 decibels. Between the 100 decibels, the ear has a degree of pain, and the normal human ear feels uncomfortable at the 120 dB SPL, and the 140 dB SPL feels pain.
Once people are exposed to excessive volume for a long time, the sensitive inner ear structure will be damaged, resulting in noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL, Noise-Induced Hearing Loss).
[banner group='banner-group']


